The name of a monatomic anion consists of the stem of the element name, the suffix - ide, and then the word ion. Thus, as we have already seen, Cl − is “chlor-” + “-ide ion,” or the chloride ion. Similarly, O 2− is the oxide ion, Se 2− is the selenide ion, and so forth. 2 lists the names of some common monatomic ions. Main Difference – Cation vs Anion. Cation and Anion are opposite terms in chemistry and stand for the two main types of ions formed. An ion is a state of matter upon the loss or gain of electron(s) compared to its actual state. When elements remain in their original form, they are known as ‘atoms’. A cation is a positively charged ion, with fewer electrons than protons, while an anion is negatively charged, with more electrons than protons. Because of their opposite electric charges, cations and anions attract each other and readily form ionic compounds. Quiz to test whether you do or not know your important Cations and Anions. Chemistry AS Level. Complete List of Cation and Anions. Selenate SeO4 2-, Selenide Se 2-, Selenite SeO3 2-, Sulfate SO4 2-, Sulfide S 2-, Sulfite SO3 2-, Tartrate C4H4O6 2-, Tellurate TeO4 2-, Telluride Te 2-, Tellurite TeO3 2-, Thiosulfate S2O3 2-, Titanate TiO3 2-, Tungstate WO4 2.
Cation vs anion chart.
Click to see full answer
Considering this, how do you find the cation?
You can often determine the charge an ion normally has by the element's position on the periodic table:
- The alkali metals (the IA elements) lose a single electron to form a cation with a 1+ charge.
- The alkaline earth metals (IIA elements) lose two electrons to form a 2+ cation.
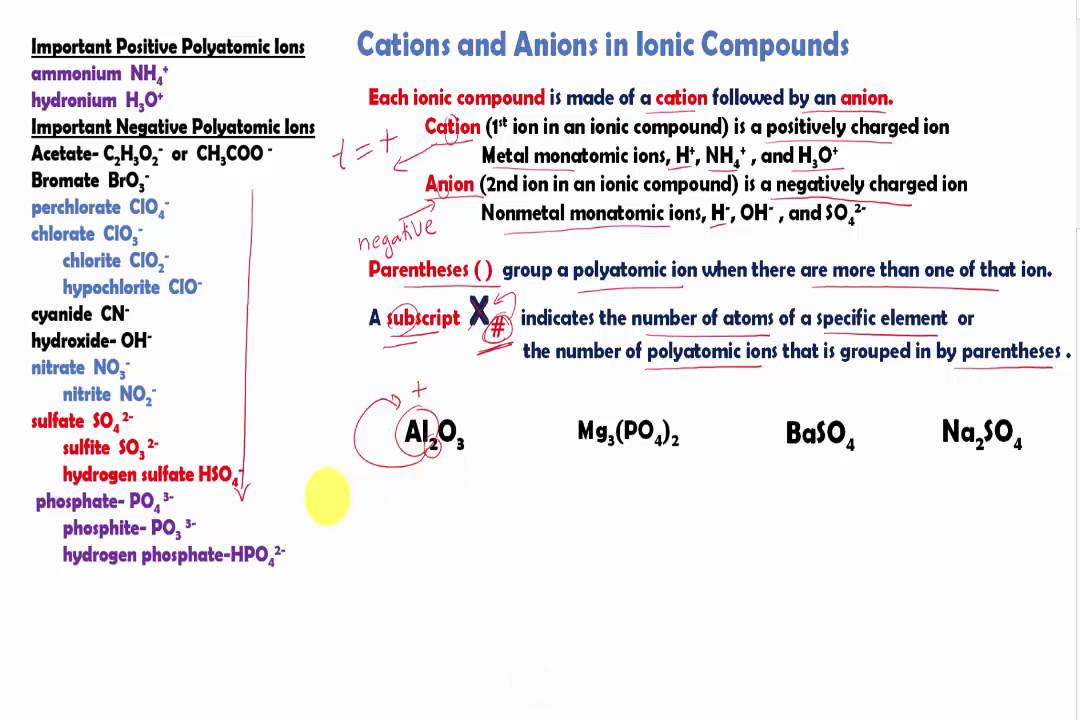
Likewise, what is an example of a cation? Examples of CationsCations can be formed from metal elements, as well as nonmetal elements. If a metal element forms an ion, it always forms a cation. Some metals always form the same type of cation. For example, sodium always forms a +1 cation and magnesium always forms a +2 cation.
Likewise, how do you find the charge of cations?
To find the ionic charge of an element you'll need to consult your Periodic Table. On the Periodic Table metals (found on the left of the table) will be positive. Non-metals (found on the right) will be negative.
What's the difference between a cation and anion?
Cations and anions are both ions. The difference between a cation and an anion is the net electrical charge of the ion. If the chemical species has more protons than electrons, it carries a net positive charge. If there are more electrons than protons, the species has a negative charge.
4- :Ferrocyanide

 3- :
3- :Se Cation Or Anion Table
Antimonide
2- :
Arsenite
1- :
Acetate
+1 :
Ammonium
+2 :
Barium
Cation Anion Calculator
+3 :
Aluminum
Se Cation Or Anion Gap
+4 :Lead
+5 :
Antimony
+6 :
Polonium
+7 :
Manganese